
Indolent lymphoma also called small-cell or low-grade lymphoma is an uncommon form of lymphoma in dogs representing around 5-291 of all canine lymphoma. The most common initial symptom of multicentric lymphoma in dogs is firm enlarged non-painful lymph nodes.
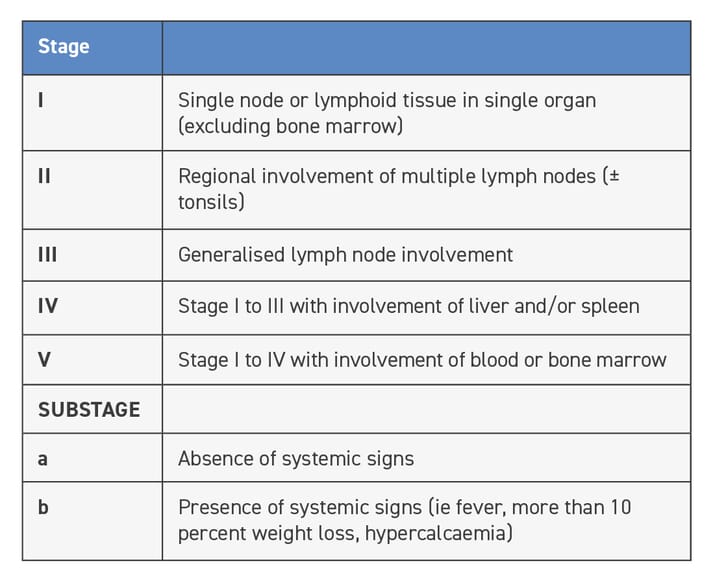
There are several stages of dog lymphoma.
What is the prognosis of lymphoma in dogs. On the other hand for dogs with stage 3 or stage 4 lymphoma who feel healthy substage a and have no blood abnormalities which includes the vast majority of dogs diagnosed with Canine Lymphoma have a very high chance of remission. But for dogs who are very sick and show lots of physical health related symptoms substage b then the chances of remission can be much less. Multicentric Lymphoma The first symptom that dogs with multicentric lymphoma usually show is swollen lymph nodes.
It is common for dogs with lymphoma to. Symptoms of canine lymphoma can vary depending on where your dogs tumor is located. Many lymphoma tumors grow in the lymph nodes.
The only symptom of this type of tumor is swelling of the lymph glands in the armpits groin and throat. Up to 80 of dogs show no other symptoms of lymphoma. Lymphoma tumors in the gastrointestinal tract can cause diarrhea vomiting decreased appetite and weight loss.
Canine epitheliotropic lymphoma may be divided into cutaneous and mucocutaneousmucosal forms. Solitary lesions have a better prognosis. Dogs with multiple lesions appear to benefit from chemotherapy and retinoid treatment with those attaining.
In her characteristic compassionate way she shares the types signs diagnosis treatment and prognosis for lymphoma in dogs with a special emphasis on multicentric lymph node lymphoma. To his parents 10-year-old Basset Hound mix Joshua was the picture of health. When he visited me for his annual exam they said he was acting like his normal silly slobbery self.
They had no concerns. Commonly the first symptoms of lymphoma include swollen lymph nodes glands and excessive drinkingpeeing. Treatment is available to extend the life of a dog with lymphoma but sadly the condition is eventually always fatal.
Contact your vet if you notice your dog has big lymph nodes. As noted in the section on Canine Lymphoma Types most Canine Lymphoma cases are B-Cell Lymphoma the phenotype that responds best to conventional treatments that are available. One staging test that Dr.
Freeman usually does NOT recommend for her patients is a Bone Marrow Aspirate. This particular staging test is actually an invasive procedure that can put unnecessary stress and. Lymphoma of the skin tissue is usually the most obvious to diagnose as it can sometimes be seen and felt as red lumps on the skin.
This is rare but lymphoma can actually affect any part of your dogs lymph tissue. Bones liver mouth eyes. Sadly this illness doesnt take prisoners.
There are several stages of dog lymphoma. You should always consult your vet to learn. More dog lymphoma symptoms include polyuria and lethargy.
When the pet owner needs proper diagnosis they will be requested to come with a detailed report of the dogs history. When at the animal hospital the medical experts will perform needle aspiration of the affected nodes to know the Lymphoma level. The prognosis for lymphoma in younger people is better than in older people.
Whenever you see a survival rate of 95 percent it tends to be among a young otherwise healthy population. Women generally have higher survival rates and more positive prognoses than men. An oncologist may or may not take a patients current health into account when providing a formal prognosis but.
The most common symptoms of lymphoma in dogs include lymph node enlargement lethargy and weight loss. The treatment of choice for lymphoma is chemotherapy. The life expectancy of dogs with lymphoma without treatment averages around 1 month and the life expectancy with chemotherapy treatment averages around 1 year.
Signs of lymphoma in dogs The most common sign of the multicentric form of lymphoma is enlarged lymph nodes commonly those located underneath the chin and on the back of the leg behind the knee of the dog. In some cases multiple lymph nodes are enlarged. Indolent lymphoma also called small-cell or low-grade lymphoma is an uncommon form of lymphoma in dogs representing around 5-291 of all canine lymphoma.
The subtypes described include follicular lymphoma marginal zone lymphoma mantle zone and T-zone lymphoma which are all derived from B-cells except for T-zone lymphoma which is T-cell in origin. What is lymphoma in dogs. Lymphoma is a cancer of the lymphatic system.
The lymphatic system is amongst other things involved in immunity and fighting infections. Lymphoma arises from cells in the lymphatic system called lymphocytes which normally travel around the body so this form of cancer is usually widespread. Alimentary lymphoma- It occurs in the gastrointestinal tract of dogs.
It can become fatal if the tumor is situated near the small or large intestine since it can restrict the passage of bowel and pose health hazards. Symptoms Gastrointestinal lymphoma accounts for approximately 5 of cases and is less easily diagnosed than the more common. Lymphoma is pretty common in dogs ranking as the third most commonly occurring cancer in canines.
Of all the conditions that cause abnormal cell growth in dogs lymphoma accounts for about 24 which is approximately 13-24 canines per 100000. Dogs can suffer from this type of cancer at any age although dogs aged 6-9 years are more susceptible. Male and female canines are both equally at.
Canine lymphoma of the rectum is associated with a favourable prognosis. Immunohistochemical evaluation of these lesions was consistent with B-cell lymphoma in all cases in which it was examined. Rectal lymphoma in 11 dogs.
A retrospective study J Small Anim Pract. Epub 2012 Aug 8. Authors N Van den Steen 1 D Berlato G.
The most common initial symptom of multicentric lymphoma in dogs is firm enlarged non-painful lymph nodes. A lymph node affected by lymphoma will feel like a.